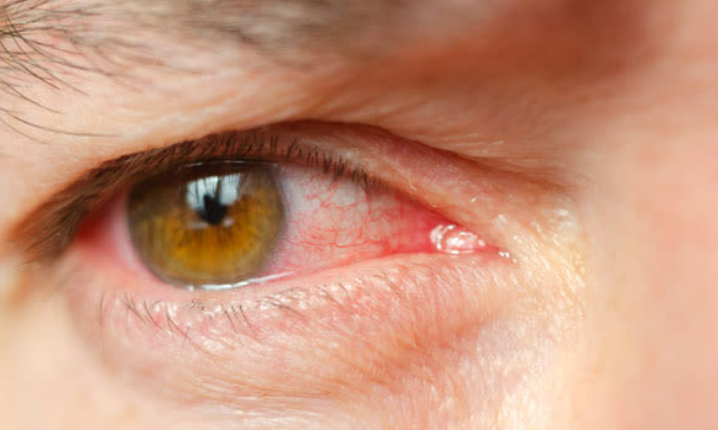
Understanding Eye Infections: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
Eye infections are common conditions that can affect anyone, causing discomfort and potentially leading to serious complications if not treated promptly. They occur when harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi, invade the eye or surrounding areas. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures for eye infections is crucial for maintaining good eye health.
Common Causes of Eye Infections
Eye infections can be caused by a variety of factors:
- Bacterial Infections: Bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae are common culprits. They can lead to conditions such as conjunctivitis (pink eye), which is characterized by inflammation of the eye’s conjunctiva.
- Viral Infections: Viruses, including adenoviruses, can cause viral conjunctivitis, which is highly contagious. Herpes simplex virus can also affect the eye, leading to a condition known as herpes keratitis.
- Fungal Infections: Fungal eye infections are less common but can occur, especially in people who wear contact lenses or have a weakened immune system. These infections are often caused by fungi like Fusarium and Aspergillus.
- Parasitic Infections: Rarely, parasites such as Acanthamoeba can cause serious infections, particularly in contact lens wearers who use contaminated water to clean their lenses.
Symptoms of Eye Infections
The symptoms of an eye infection can vary depending on the type of infection but commonly include:
- Redness in the eye
- Itching or burning sensation
- Watery or thick discharge from the eye
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Pain or discomfort in the eye
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical attention to prevent the infection from worsening.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing eye infections involves adopting good hygiene practices and being mindful of eye health. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of eye infections:
- Wash Your Hands: Regularly washing your hands with soap and water can help prevent the spread of infectious agents to your eyes.
- Avoid Touching Your Eyes: Refrain from touching or rubbing your eyes, especially with unclean hands, as this can introduce bacteria or viruses.
- Proper Contact Lens Care: If you wear contact lenses, follow the prescribed cleaning and storage instructions. Avoid using tap water to clean lenses and never sleep with lenses unless they are designed for overnight wear.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, eye makeup, or eye drops with others, as this can spread infections.
- Use Protective Eyewear: When swimming, use goggles to protect your eyes from contaminated water. Also, wear protective eyewear in environments where your eyes could be exposed to irritants or debris.
Treatment for eye infections depends on the underlying cause. Bacterial infections may require antibiotic eye drops or ointments, while viral infections often resolve on their own but may need antiviral medications in severe cases. Fungal and parasitic infections may require specific antifungal or antiparasitic treatments. It’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
Eye infections, while often not severe, can cause significant discomfort and potentially lead to serious complications if untreated. Recognizing the symptoms early and taking preventive measures can help protect your eyes. Maintaining good hygiene, practicing proper contact lens care, and seeking medical advice at the first sign of an infection are essential steps in safeguarding your eye health.